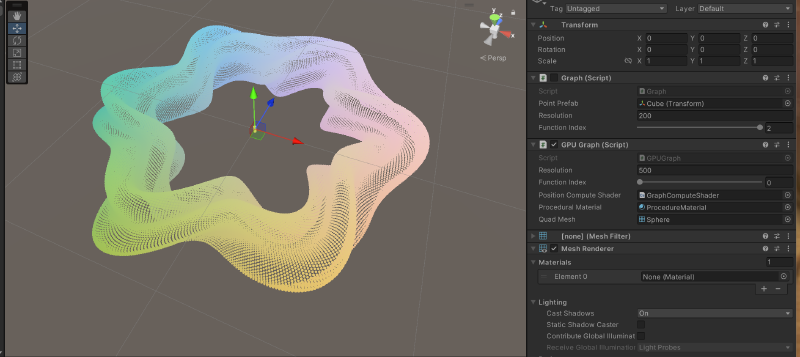
【Catlike Coding】Compute Shader
学了Catlike Coding的basic部分, compute shader部分有点收获,写个总结.
GPUGraph.cs
通过Shader.propertyToID把数据从C#脚本中传递到shader中(CPU To GPU).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
|
using UnityEngine;
//This is a script to draw a 3D graph by GPU, using simple mesh.
public class GPUGraph : MonoBehaviour
{
// [SerializeField] Transform pointPrefab; // Unused in procedural rendering but kept for reference
[SerializeField] int resolution = 200;
[SerializeField, Range(0, 2)] private int functionIndex = 0;
[SerializeField] ComputeShader positionComputeShader;
[SerializeField] Material proceduralMaterial;
[SerializeField] Mesh quadMesh;
ComputeBuffer positionBuffer;
static readonly int
PositionsID = Shader.PropertyToID("_Positions"),
ResolutionID = Shader.PropertyToID("_Resolution"),
TimeID = Shader.PropertyToID("_Time"),
FunctionIndexID = Shader.PropertyToID("_FunctionIndex"); // Added for function selection
private void Awake()
{
// Initialize ComputeBuffer with resolution * resolution elements, each a Vector3 (3 floats)
positionBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(resolution * resolution, 3 * sizeof(float));
}
void Update()
{
UpdatePositions();
ProcedureDraw();
}
void UpdatePositions()
{
// Calculate thread groups based on resolution, assuming Compute Shader uses 16x16 threads
int threadGroupsX = Mathf.CeilToInt(resolution / 16.0f);
int threadGroupsY = Mathf.CeilToInt(resolution / 16.0f);
// Set Compute Shader parameters
positionComputeShader.SetInt(ResolutionID, resolution);
positionComputeShader.SetFloat(TimeID, Time.time);
positionComputeShader.SetInt(FunctionIndexID, functionIndex); // Set the function index
// Set the buffer and dispatch the Compute Shader
int kernel = positionComputeShader.FindKernel("CalculatePositions");
positionComputeShader.SetBuffer(kernel, PositionsID, positionBuffer);
positionComputeShader.Dispatch(kernel, threadGroupsX, threadGroupsY, 1);
// Vector3[] positions = new Vector3[resolution * resolution];
// positionBuffer.GetData(positions);
// Debug.Log("Position[0]: " + positions[0]);
}
void ProcedureDraw()
{
// Ensure the material has the latest position buffer
proceduralMaterial.SetBuffer("_Positions", positionBuffer);
// Draw instanced meshes procedurally
Graphics.DrawMeshInstancedProcedural(
quadMesh,
0,
proceduralMaterial,
new Bounds(Vector3.zero, Vector3.one * 10f),
resolution * resolution
);
}
private void OnDestroy()
{
// Release the buffer to prevent memory leaks
positionBuffer.Release();
}
}
|
GraphComputeShader.compute
compute shader 计算好坐标,并返回给缓冲区
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
|
#pragma kernel CalculatePositions
RWStructuredBuffer<float3> _Positions;
uint _Resolution;
float _Time;
uint _FunctionIndex; // 注意:这里是 __FunctionIndex,与你的代码保持一致
#define PI 3.14159265358979323846
// 函数1:原始的绘图函数
float3 Function1(float u, float v, float time)
{
float r1 = (7.0 + sin(PI * (6.0 * u + time / 2.0))) / 10.0;
float r2 = (3.0 + sin(PI * (4.0 * v + 8.0 * u + 2.0 * time))) / 20.0;
float s = r1 + r2 * cos(PI * v);
float3 position;
position.x = s * sin(PI * u);
position.z = s * cos(PI * u);
position.y = r2 * sin(PI * v);
return position;
}
// 函数2:示例函数(简单平面)
float3 Function2(float u, float v, float time)
{
float3 position;
position.x = u;
position.y = 0.0;
position.z = v;
return position;
}
// 函数3:示例函数(波浪面)
float3 Function3(float u, float v, float time)
{
float3 position;
position.x = u;
position.y = sin(u * 5.0 + time) * 0.5;
position.z = v;
return position;
}
// 线程组配置
[numthreads(16, 16, 1)]
void CalculatePositions (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
// 索引保护,避免越界
if (id.x >= _Resolution || id.y >= _Resolution) return;
// 归一化计算,确保 u 和 v 在 [-4, 4] 范围内
float step = 8.0 / (_Resolution - 1);
float u = -4.0 + step * id.x;
float v = -4.0 + step * id.y;
// 根据 __FunctionIndex 选择不同的绘图函数
float3 position;
switch (_FunctionIndex)
{
case 0:
position = Function1(u, v, _Time);
break;
case 1:
position = Function2(u, v, _Time);
break;
case 2:
position = Function3(u, v, _Time);
break;
default:
position = float3(0, 0, 0); // 默认值,防止未定义行为
break;
}
// 计算缓冲区索引并写入结果
uint index = id.y * _Resolution + id.x; // 行优先存储
_Positions[index] = position;
}
|
Catlike shader 是surface shader,在我2022 URP Unity中不能使用. 所以我让AI改为了
URP shader.
通过
1
2
3
|
#if defined(UNITY_PROCEDURAL_INSTANCING_ENABLED)
// Get the position for this instance
float3 position = _Positions[unity_InstanceID];
|
来获取缓冲区内的坐标,然后改变unity object to world 矩阵, 来改变坐标. 挺巧妙的.
ProcedureDraw.shader
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
|
Shader "Custom/ProceduralSurfaceURP" {
Properties {
_Scale ("Instance Scale", Range(0.001, 0.05)) = 0.005
}
SubShader {
Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" "RenderPipeline"="UniversalPipeline" }
Pass {
HLSLPROGRAM
#include "Packages/com.unity.render-pipelines.universal/ShaderLibrary/Core.hlsl"
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#pragma multi_compile_instancing
#pragma instancing_options procedural:ConfigureProcedural
#pragma target 4.5
#if defined(UNITY_PROCEDURAL_INSTANCING_ENABLED)
StructuredBuffer<float3> _Positions; // Buffer to receive positions from C#
#endif
float _Scale;
struct Attributes {
float4 positionOS : POSITION;
UNITY_VERTEX_INPUT_INSTANCE_ID
};
struct Varyings {
float4 positionCS : SV_POSITION;
float3 worldPos : TEXCOORD0;
};
void ConfigureProcedural() {
#if defined(UNITY_PROCEDURAL_INSTANCING_ENABLED)
// Get the position for this instance
float3 position = _Positions[unity_InstanceID];
// Build the transformation matrix: scale and translate
float4x4 mat = float4x4(
_Scale, 0, 0, position.x,
0, _Scale, 0, position.y,
0, 0, _Scale, position.z,
0, 0, 0, 1
);
// Apply the transformation to UNITY_MATRIX_M (object to world matrix)
UNITY_MATRIX_M = mat;
#endif
}
Varyings vert(Attributes input) {
Varyings output;
UNITY_SETUP_INSTANCE_ID(input);
output.positionCS = TransformObjectToHClip(input.positionOS.xyz);
output.worldPos = TransformObjectToWorld(input.positionOS.xyz);
return output;
}
half4 frag(Varyings input) : SV_Target {
half3 color = 0.5 + 0.5 * sin(input.worldPos);
return half4(color, 1);
}
ENDHLSL
}
}
}
|
总结
这一套方案让CPU运算量大大降低. 戴森球的优化应该也采用类似的方法, 把各种CPU的计算转移到GPU中进行.
大概效率提升了一个数量级.
戴森球作者发的专栏
https://www.zhihu.com/question/442555442/answer/1711890146?utm_psn=1883875216381432992